About us
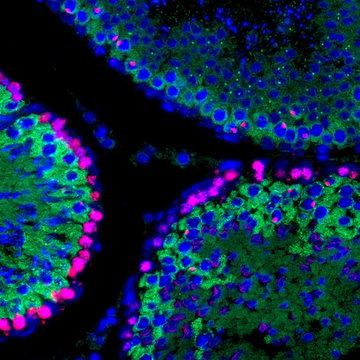
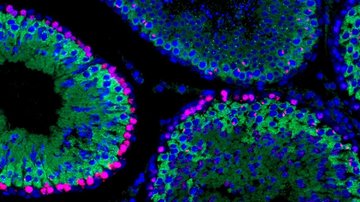
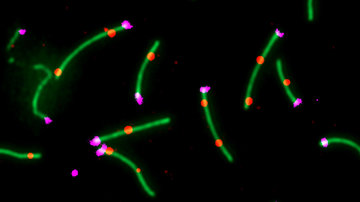
The current fertility studies in model mammals move from the effects of single gene to genetic interactions important for human reproductive medicine that occur during spermatogenesis and oogenesis.
The Prdm9 gene (also called Meisetz) is necessary for both male and female meiosis and fertility in the laboratory mouse. The biochemical function of the PRDM9 protein is to methylate histones. The mouse, bovine, and human PRDM9 proteins specify the sites of meiotic recombination. However, PRDM9 is dispensable for fertility in the dog. PRDM9 polymorphisms were revealed in sterile human patients and PRDM9 variation contributes to instability of the human genome. We have identified Prdm9 as the first vertebrate hybrid sterility gene. Different Prdm9 mutations display different stages and degrees of spermatogenetic arrest on various backgrounds, indicating that the resulting phenotype is dependent on genetic interactions of Prdm9.
The aims of the project are: analyses of genes regulating germ cell development in mouse and rat testes and ovaries, interspecific differences important for translation studies; analyses of interactions and incompatibilities of genes expressed in testes and ovaries; analyses of models of germ cell development defects that are affected by Prdm9, including complete meiotic arrest (azoospermia), limited fertility (reduced sperm count – oligospermia), sperm head malformations (teratozoospermia), and reproductive age defects (time-dependent arrest of germ cell development).
Videoabstract of a current paper (Flachs et al 2014, in Czech with optional English subtitles)