About us
Using genetically modified mouse models and gene expression profiling, we identify molecular targets for the development of preventive and diagnostic strategies.
This project focuses on
- transcriptional regulation in neurosensory development and maintenance in the inner ear model
- the molecular mechanisms involved in pathologies associated with diabetes mellitus
- the molecular causes of abnormal embryonic development
Research Objectives
- To identify molecular changes induced by the diabetic exposure.
- To identify target genes for pathological changes in embryonic development.
- To identify genes, contributing to developmental defects and heart dysfunctions in diabetic pregnancies.
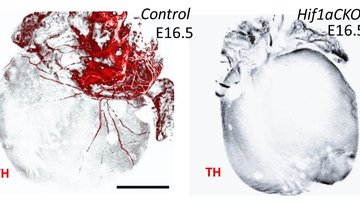
- To examine HIF-1α function in molecular responses to diabetes.
The number of people with diabetes was estimated to be 53 million, or 8.1% of the adult population in Europe in 2011. Both type 1 and type 2 diabetes are associated with a majority of risk health factors, such as hypertension, hyperlipidemia, obesity, thrombosis, autonomic neuropathy, nephropathy, endothelial dysfunction, and microvascular pathology.
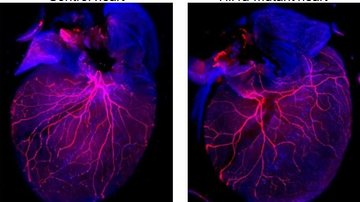
Hyperglycemia triggers diabetic tissue damage, including microvascular complications characterized by the increased risk of cardiomyopathy and myocardial infarction, and nephropathy. Hypoxia is another important pathophysiological factor associated with diabetic complications. Transcriptional responses to hypoxia are mediated by hypoxia inducible factor 1 (HIF-1). HIF-1 activates over 800 target genes that are involved in cell proliferation, angiogenesis, glycolytic energy metabolism, and apoptosis. HIF-1 consists of two subunits, the regulatory subunit HIF-1α, and constitutively expressed HIF-1β. Oxygen tension plays a key role in the regulation of HIF-1α expression, stabilization, and activation. The aim of our research is to examine HIF-1α function in molecular responses to diabetes. We are interested in cardiac responses associated with diabetic cardiomyopathy. We are also analyzing the changes induced by the diabetic environment in kidneys resulting in diabetic nephropathy.
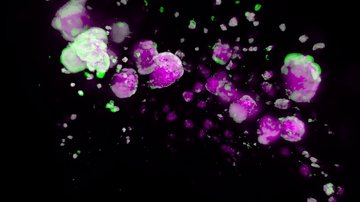
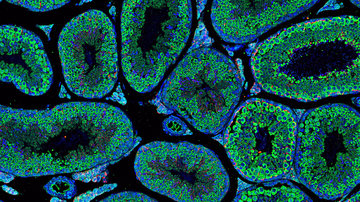
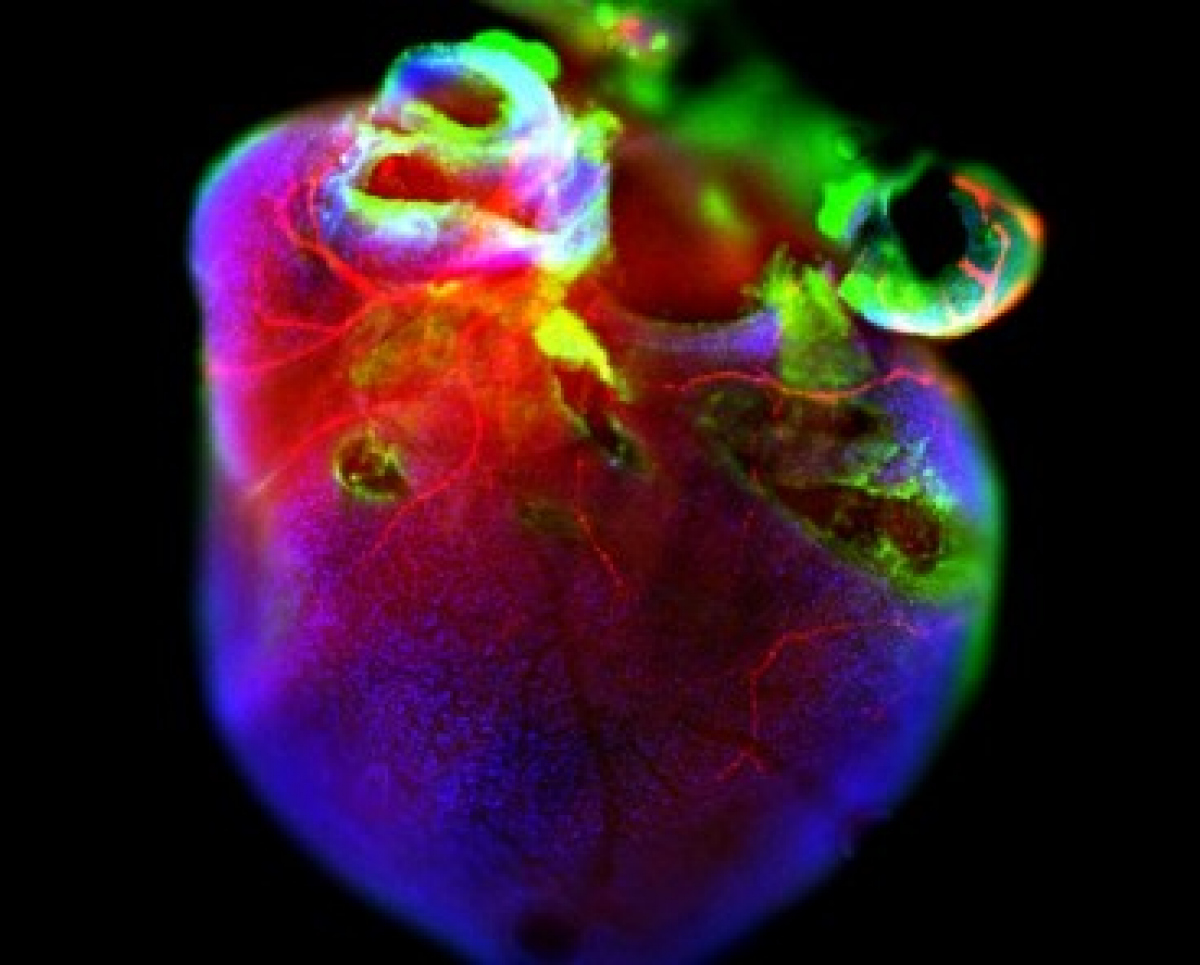
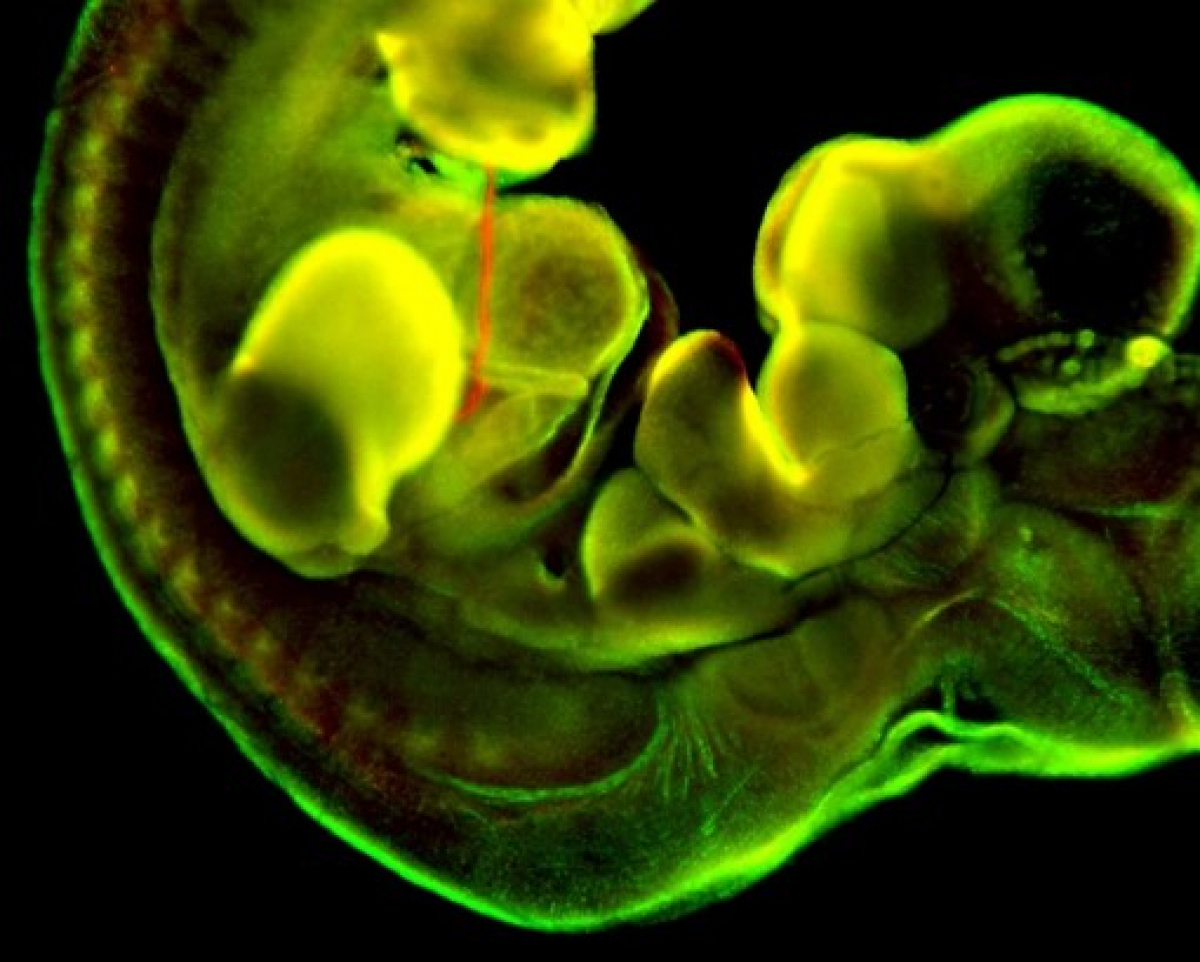
Diabetes of mother represents a serious complication for developing embryo. Diabetic pregnancy is associated with an increased incidence of congenital malformations compared with non-diabetic pregnancy. Diabetic embryopathy can affect any developing organ system, although congenital heart defects and neural tube defects are the most frequent malformations in the children of diabetic women. Even without congenital abnormalities, the risk for diabetes and cardiovascular disease is elevated in children and adults who have been exposed to adverse intrauterine conditions. This phenomenon is also termed fetal or developmental programming. However, the molecular mechanisms by which maternal diabetes induces changes in embryos remain unclear. The overarching goal of our research has been to identify key molecular players in changes caused by the exposure to diabetes. Using the mouse as an experimental system and global gene expression profiling, we have identified target genes, which can serve as an indicator for specific abnormalities in heart development and function, and genes, contributing to developmental heart defects in diabetic pregnancies and heart dysfunctions in the adult.
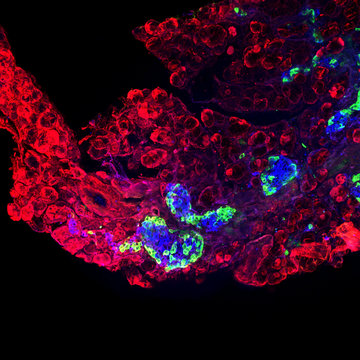
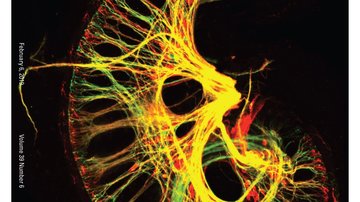
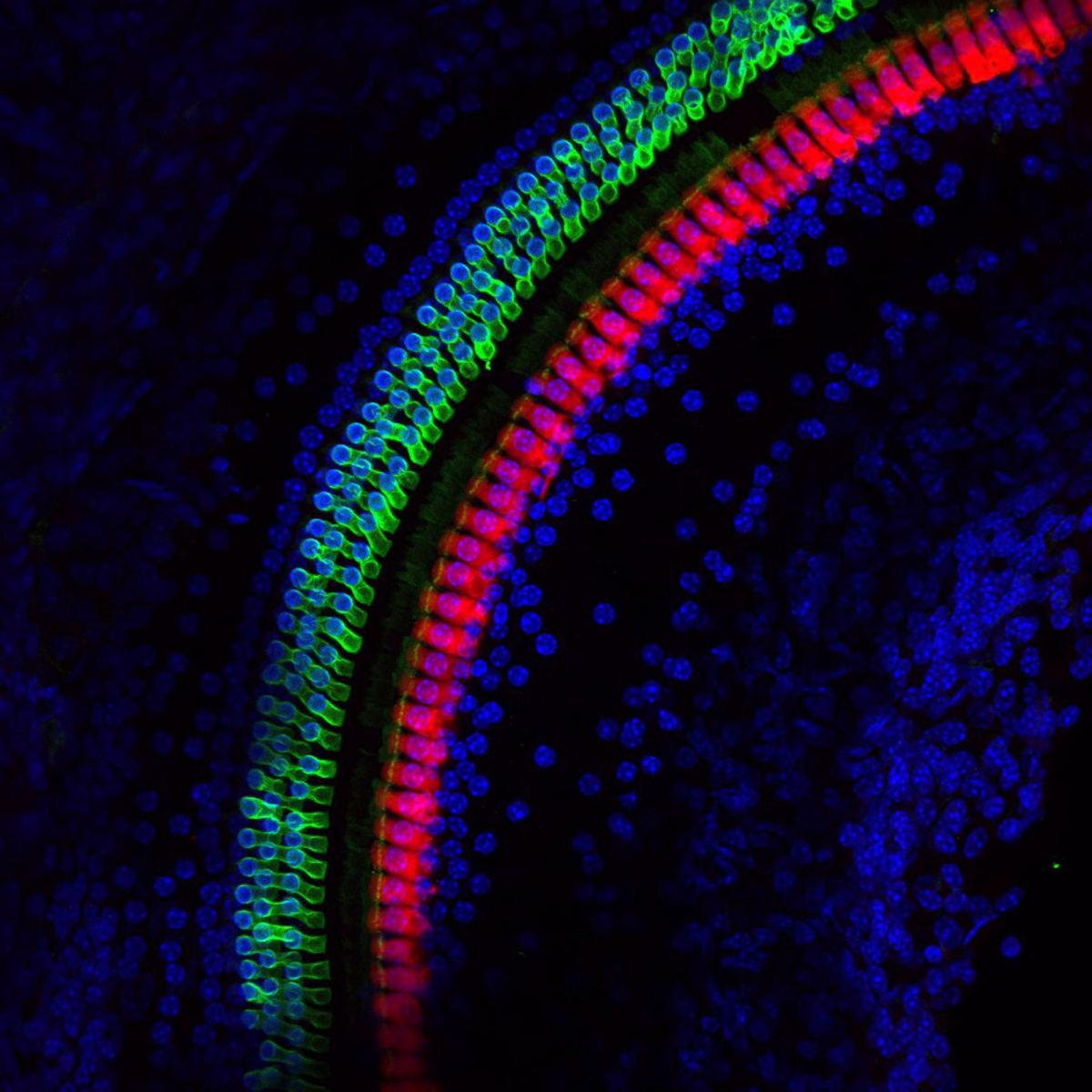
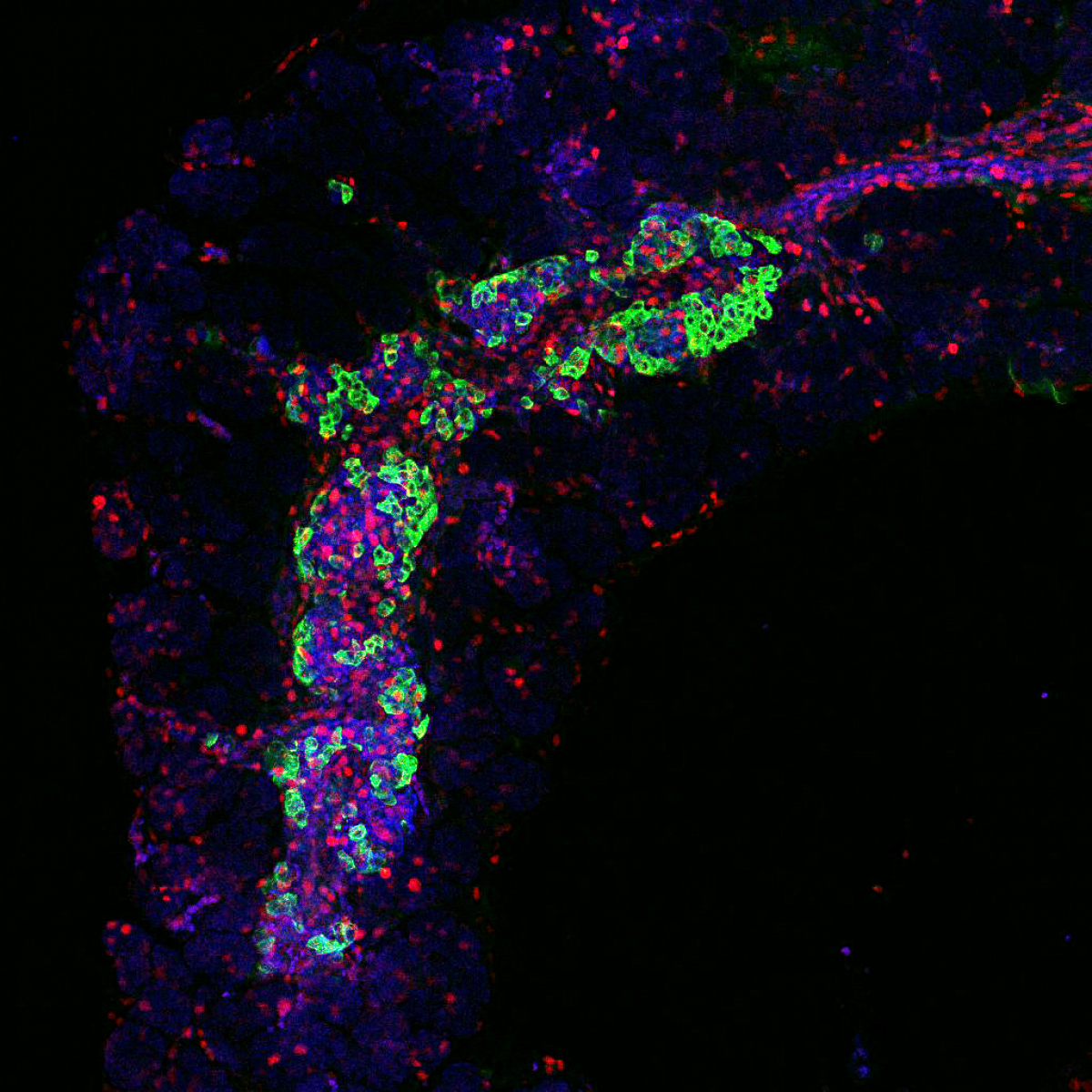
Our second major project focuses on transcriptional regulation in neurosensory embryonic development. Specifically, we are interested in identifying genes and pathways that are crucial in generating specific cell types in the inner ear. This is a critical step for understanding the pathophysiology of hearing disorders, associated with the death of hair cells, supporting cells, neurons and the loss of neuronal contacts. Approximately 71 million Europeans have a hearing impairment. Using mouse model, we analyze the interactions and cooperation of transcription factors, ISLET1, SOX2, and bHLH neurosensory specification factors, in the development of the neuronal and sensory lineages of the inner ear.
Follow us on Twitter: @PavlinkovaLab